Are you sure you can spot a deepfake? Study says people are too confident
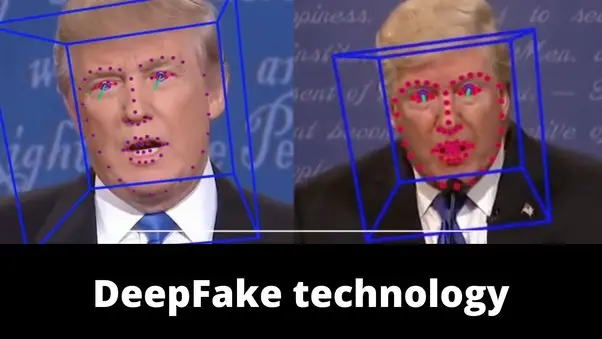
Example of a Deep Fake: a risk to our digital presence
Users think they can easily spot fake videos or photos, and that's dangerous. Joe Biden dressed as a woman and drinking Bud Light; Donald Trump playing a shady lawyer in the series "Breaking Bad": the two most likely contenders in the 2024 US presidential election have recently been the subject of fake videos.
The product of "generative" artificial intelligence tools such as ChatGPT, "deepfakes" or synthetic images "have reached a level of sophistication that prevents them from being detected with the naked eye," say the authors of a recent multinational study, according to which people are too confident in their own ability to detect a fake.
The 2023 Online Identity Study, published at the end of May and conducted by Censuswide for Jumio, an online security company based in California, collected the opinions of more than 8,000 people in Great Britain, Mexico, Singapore and the United States about "deepfakes."
About two-thirds of respondents said they were familiar with the technology, though the percentage ranged from 56 percent in Britain to almost 90 percent in Singapore. More than half said they were confident they could tell the difference between an authentic video and a fake.
Deepfakes used by scammers are very dangerous
Perhaps they shouldn't be so sure of themselves. “Deepfakes are getting better and harder to spot without the help of artificial intelligence,” says Stuart Wells, Chief Technology Officer at Jumio.
While fakes involving public figures are likely to be quickly detected as such, the same is not always true for low-profile scams targeting personal finances or identity.
Less than half of respondents in Britain and the UK were aware that AI could pose a threat when it comes to identity theft and other money-stealing schemes.
The survey team described the figures as “worrying,” pointing to data from financial association UK Finance, which indicates that identity theft scams amounted to $220 million in 2022. According to the US Federal Trade Commission, US consumers lost $2.6 billion in the same year.
What are the characteristics of deepfakes? Do deepfaking refer to videos, audio, or images created using a form of artificial intelligence called deep learning?All related
Deepfakes refer to media (videos, audio, images) that are manipulated or generated using deep learning techniques, often involving artificial intelligence algorithms known as deep neural networks.
These AI algorithms analyze and synthesize existing data to create realistic, but entirely fabricated, content. Characteristics of deepfakes include:
- Realistic Appearance: Deepfakes are often highly convincing, making it challenging to discern them from authentic media. They exhibit realistic facial expressions, gestures, or audio characteristics of the targeted individual.
- Face Swapping: In video deepfakes, the most common form involves face swapping, where one person's face is replaced with another's seamlessly, utilizing advanced facial recognition and synthesis techniques.
- Voice Cloning: Audio deepfakes use AI to mimic someone's voice by analyzing existing recordings. They can generate synthetic speech that sounds like the targeted individual, allowing manipulation of spoken content.
- Manipulated Content: Deepfakes can alter context, change expressions, create scenarios that never occurred, or make individuals appear to say or do things they never did.
- Accessibility: The proliferation of deep learning techniques and accessible tools has made creating deepfakes more widespread and accessible to individuals without advanced technical expertise.
While deepfakes can have benign uses like entertainment and creative content, they also pose significant risks, especially in spreading misinformation, manipulation, and privacy breaches. Technologies to detect and counteract deepfakes are continually evolving to address these concerns.
Here are some key characteristics of deep fakes:
1. Highly convincing: Deepfakes can be incredibly convincing, thanks to the advancements in deep learning technology. They can seamlessly blend faces, voices, and body movements onto existing videos or images, making it difficult to distinguish them from the real thing.
2. Malicious intent: While not always the case, deepfakes are often used with malicious intent. They can be used to spread misinformation, damage reputations, or even commit fraud. For instance, deepfakes of politicians have been used to sway public opinion, and deepfakes of celebrities have been used in scams.
3. Increasing sophistication: As deep learning technology continues to evolve, so too do deepfakes. This makes them even harder to detect and raises concerns about their potential for harm.
4. Not just video: Although video is the most common format for deepfakes, they can also be created for audio and images. Deepfakes of voices can be used to impersonate real people, and deepfakes of images can be used to manipulate reality in subtle but potentially harmful ways.
5. Detection challenges: Identifying deepfakes can be challenging, even for experts. However, there are certain telltale signs to look for, such as:
- Unnatural movements or facial expressions: Deepfakes often struggle to replicate the subtle nuances of human movement and expression.
- Blurring or inconsistencies around manipulated areas: The technology used to create deepfakes isn't perfect, and it can sometimes leave behind telltale artifacts.
- Inconsistencies with audio or lip-syncing: If the audio doesn't match the lip movements, it could be a sign of a deepfake.
Deepfakes are a complex and evolving phenomenon with both positive and negative potential. Being aware of their characteristics and the challenges in detecting them is crucial in today's digital age.
I hope this information was helpful! Let me know if you have any other questions.
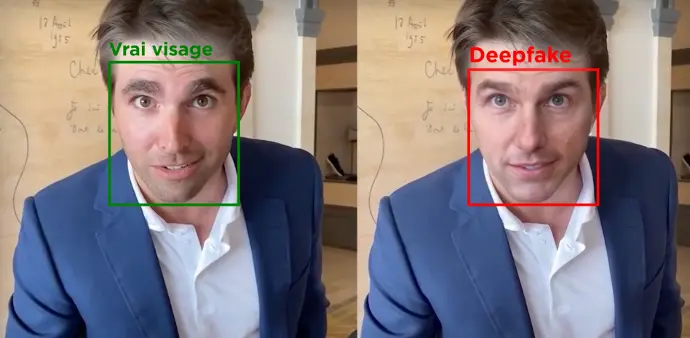
If you observe the deepfake image, you'll notice a significant degradation in quality with low pixel resolution. Zooming in and out reveals notable differences between the original and deepfake images.
Deepfakes typically refer to media, including videos, audio, or images, created using deep learning, a subset of artificial intelligence. The characteristics of deepfakes include realistic alterations of facial features, expressions, voice, and overall content, often making it challenging to distinguish from authentic content. Deepfakes leverage advanced algorithms and neural networks to manipulate and generate convincing synthetic media.

 IHRO NEWS
IHRO NEWS