
Technology and Digital World, Digital Human Rights
Ensuring the protection of human rights in the digital age

Statements by the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights
1 part Artificial Intelligence and the future of Humanity & the new world
2 part Artificial Intelligence and the future of Humanity & the new world
We invite you to read our Reports on our work at the international level and the measures necessary to protect the rights of every citizen of the world.
Artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence is a system created by humans that constitutes a non-living rational agent. Rationality, in this case, is understood as the ability to maximize an expected result.
Artificial intelligence, therefore, consists of the design of processes that, when executed on a physical architecture, produce results that maximize a certain measure of performance. These processes are based on sequences of inputs that are perceived and stored by the aforementioned architecture.
It should be noted that intelligence is linked to knowing how to choose the best options to solve some type of problem. There are various types of intelligence according to their attributes and processes, such as operational intelligence, biological intelligence or psychological intelligence.
Artificial, on the other hand, is an adjective that indicates that which is made by the hand, art or ingenuity of man. Artificial also allows us to name that which is unnatural or false.
Artificial Intelligence in Law: Real-World Applications of the Technology

Digital rights

Biometrics

Artificial Intelligence in Justice: Robot Judges and their Impact
The Impact of AI on Law Enforcement, Criminology and Criminal Justice

AI in the Fight Against Human Trafficking and Forced Labor

Artificial intelligence in medical health

Artificial Intelligence Cryptocurrencies
Artificial Intelligence vs. Humans: Differences and Risks

All Drones and Human Rights

Artificial Intelligence in War Conflicts

AI in Humanitarian Assistance

Teleworking

Artificial Intelligence in Journalism

Artificial Intelligence in agriculture

Artificial intelligence and education

Artificial Intelligence and manufacturing

Artificial intelligence in sport

How Artificial Intelligence Could Widen the Gap Between Rich and Poor Nations
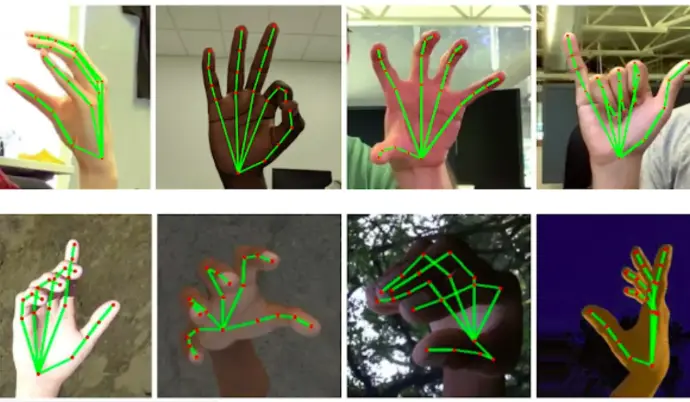

Artificial Intelligence for Sign Language
Human-Robot Interaction
Artificial intelligence and its impact on the jobs of the future and Unemployment due to artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) will affect almost 40% of jobs worldwide, replacing some and complementing others. To harness this potential, policies must strike a fine balance.
Artificial intelligence and employment: perspectives and opportunities

AI Collaborator: Optimizing Work Performance



IMF warns that AI will bring long-term unemployment and calls for redistributive taxes

Artificial Intelligence in the World System: What Will Happen to Employment, Wages, and Democracy?

Human rights must be respected both online and offline. Digital technologies provide new means to exercise human rights, but are too often also used to violate them. Data protection and privacy, digital identity, the use of surveillance technologies, and online violence and harassment are issues of particular concern.
ENSURING THE PROTECTION OF HUMAN RIGHTS
Human rights apply both online and offline. Digital technologies provide new means to exercise human rights, but they are too often used to violate human rights. Data protection and privacy, digital identity, the use of surveillance technologies, online violence and harassment, are of particular concern.
THE WAY FORWARD
1. PLACE HUMAN RIGHTS AT THE CENTRE of regulatory frameworks and legislation on digital technologies.
2. GREATER GUIDANCE ON THE APPLICATION OF HUMAN RIGHTS STANDARDS in the digital age
3. ADDRESS PROTECTION GAPS CREATED BY EVOLVING DIGITAL TECHNOLOGIES
4. DISCOURAGE BLANKET INTERNET SHUTDOWNS and generic blocking and filtering of services
5. HUMAN RIGHTS-BASED DOMESTIC LAWS and practices for the protection of data privacy
6. CLEAR, COMPANY-SPECIFIC ACTIONS TO PROTECT PRIVACY RIGHTS and other human rights
7. ADOPT AND ENHANCE SAFEGUARDS RELATED TO DIGITAL IDENTITY
8. PROTECT PEOPLE FROM UNLAWFUL OR UNNECESSARY SURVEILLANCE
9. HUMAN-RIGHTS BASED LAWS AND APPROACHES to address illegal and harmful online content
10. TO ENSURE ONLINE SAFE SPACES, TRANSPARENT AND ACCOUNTABLE CONTENT GOVERNANCE FRAMEWORKS that protect freedom of expression, avoid overly restrictive practices and protect the most vulnerable

What risks does artificial intelligence pose?
- AI Hallucinations
- Deepfake, AI-generated art and Fake News
- AI Voice Scams AI voice scams and other dark crimes
The risks of artificial intelligence (AI)
In Europe, the law regulating artificial intelligence is now official.
General Assembly adopts landmark resolution on AI
21 March 2024 Human rights

 IHRO NEWS
IHRO NEWS
