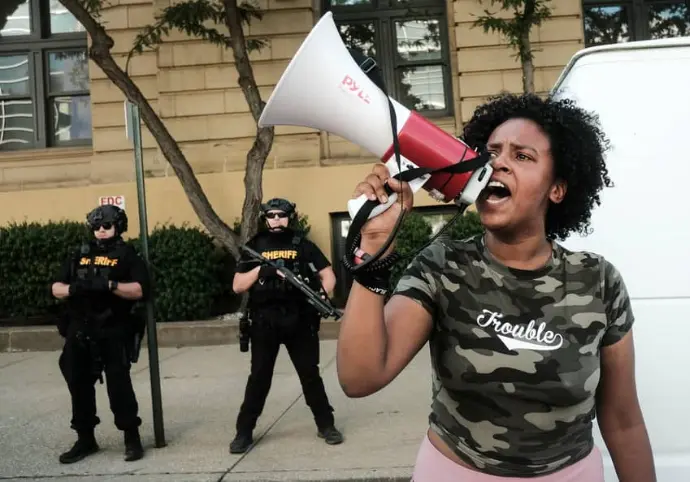Discrimination is the act and result of discriminating. This verb (discriminate), for its part, refers to treating people unequally or excluding them for gender, religious, political, racial or other reasons.
For example: "A young Muslim was a victim of discrimination in a bar", "The government will promote a new campaign against discrimination", "It is outrageous that, in the 21st century, women continue to be victims of workplace discrimination."
ORIGINS AND CONSEQUENCES OF DISCRIMINATION
Someone discriminates when they do or fail to do something, generating inequality or injustice in access to an opportunity or a resource. Discrimination, therefore, means that an individual, a group or an institution is harmed by the decision of a third party.
For discrimination to occur, there must be a sense of belonging which, in turn, causes prejudice. Whoever discriminates does not recognize the discriminated against as part of their group and intends that the other does not integrate, distance themselves and/or suffer negative consequences for belonging to another community, which is considered inferior or harmful.
SOME EXAMPLES
Suppose a nightclub prohibits dark-skinned people from entering. This act of discrimination aims to "protect" white individuals from contact with subjects who are considered inferior in terms of their social status, economic position, cultural level, etc. This is, of course, an arbitrary, unfair, irrational and even illegal measure.
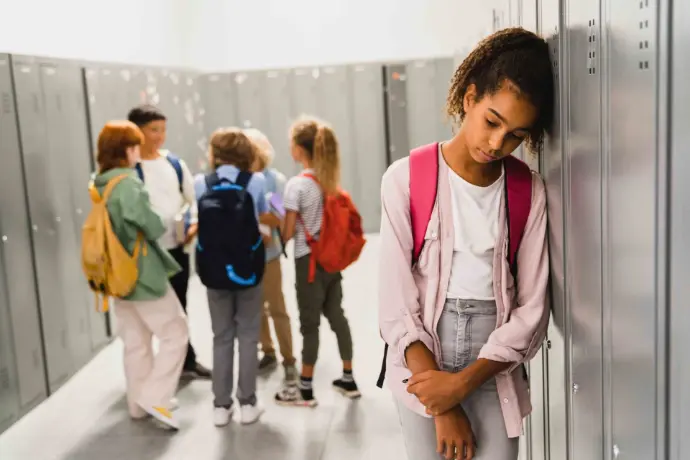
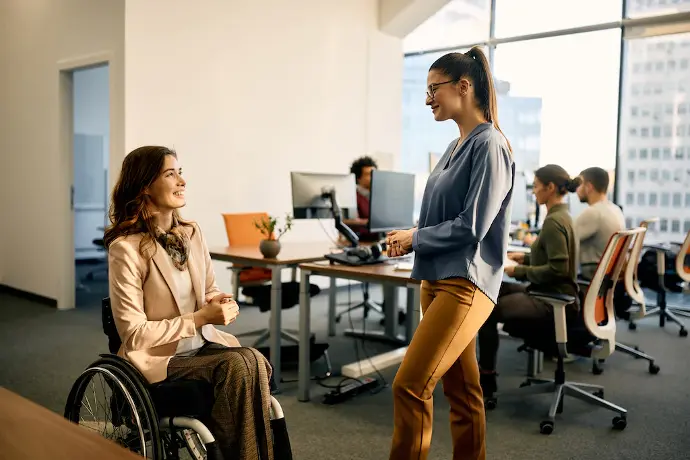
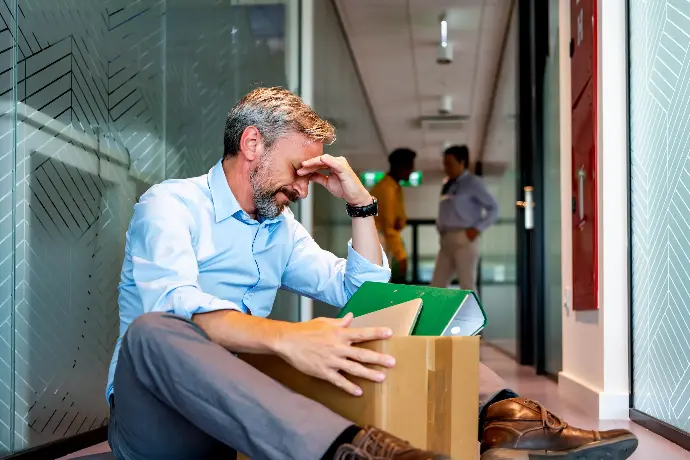
Discrimination can occur due to age (when those over 40 years of age are not allowed to access a job, to cite one case), gender (a woman who, for the same job, receives less money than a man), orientation sexual (if a homosexual couple is expelled from a restaurant), and ethnic origin (teasing a gypsy child for his way of speaking).
OTHER TYPES OF DISCRIMINATION
However, other types of discrimination can occur and be identified, among which we can highlight the following:
-Religious discrimination which, as its name indicates, is that which occurs due to the religious ideas or beliefs that a person has. Thus, for example, one of the most relevant events produced by this issue occurred in Nazi Germany where millions of Jews were locked up in a concentration camp, subjected to all types of torture and were even murdered for their faith.
-Discrimination due to disability, which is what occurs when a person with a disability is rejected either in society in general or in a job because of the physical or mental limitation they present. An example is that an individual is rejected for a job in a restaurant because, for example, he has Down Syndrome.
A BENEFIT
Finally, we speak of positive discrimination when a benefit or special protection is granted to a social group that is usually a victim of discrimination.
Currently, positive discrimination is used, above all, to achieve real equality between men and women in all areas of our society. In this case, it is considered that it allows us to achieve everything from real equity to improvements in the living conditions of women, and because it is useful for equalizing roles.
THE HUMAN BEING AND THE RACE
The concept of race is also often used in human beings. Some specialists assure, however, that the correct term to use with homo sapiens is ethnicity, while other experts maintain that ethnicity is linked to the properties of culture.
Human races are often differentiated based on visible biological characteristics such as the amount of melanin they have in their skin (that is, its color) and certain facial features. That is why in colloquial language we speak of the white race, the black race and the yellow race.
The rise of racism in Nazi Germany and other countries also contributed to the concept of race falling out of use by scientists. The main theories began to highlight that Humanity does not have isolated races due to mobility (emigration and immigration), sociability and processes of miscegenation.
SOCIETIES AND RACISM
Racism is, along with speciesism and sexism, one of the most atrocious evils that our societies experience. Although today there is much more information and, supposedly, greater freedom, many people are victims of this type of discrimination every day.
In the United States, for example, in recent times the number of racist groups has increased by more than 700%. Without going any further, years ago an organized gang that planned to assassinate then-President Barack Obama was arrested, solely because of his African-American condition.
In Spain and many European countries, where there is supposed to be greater tolerance, racism becomes xenophobia and, although laws usually protect the immigrant community, in practice they are not applied and many people suffer their consequences. People who cannot access this or that service just because of the color of their skin, for example. Proof of this is a measure taken by the Rajoy government with illegal immigrants in Spain; It denied all of them the right to a health card and, therefore, to public health, forcing them to pay for the services. There are thousands of other equally disastrous examples.
In other countries, such as Latin America, this type of discrimination targets those who come from poorer regions, from the north of the country, or who belong to aboriginal cultures.
RACE AS A FACTOR OF DISCRIMINATION
Racism exists in every corner of the earth. Humans continue to divide and humiliate those who are different, even being capable of killing because of it. Humanity boasts of being superior to animals for its ability to think and, however, and although this hypothesis has less and less basis, it is capable of destroying everything and everyone who opposes its way of living. In this case, to those who have physical characteristics different from yours.
One of the things that characterize the human species is the fear of what is different, its rejection of change and everything that may threaten its stability. For this reason, some religious people denigrate those who are not religious, saying that "they will go to hell for not believing" and trying to convert everyone to their ideology, homophobes attack homosexuals and all those open beings who accept sexual freedom, and Racists attack those who are physically and culturally different.

 IHRO NEWS
IHRO NEWS