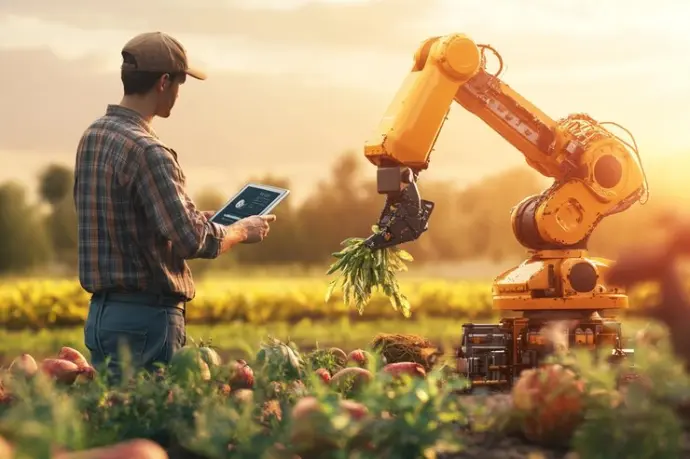
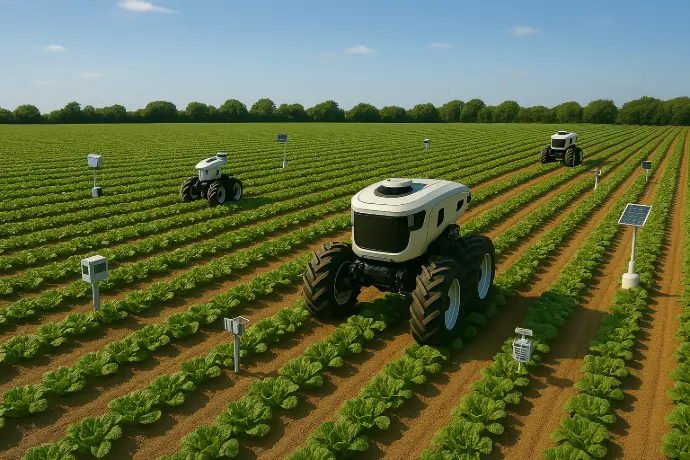
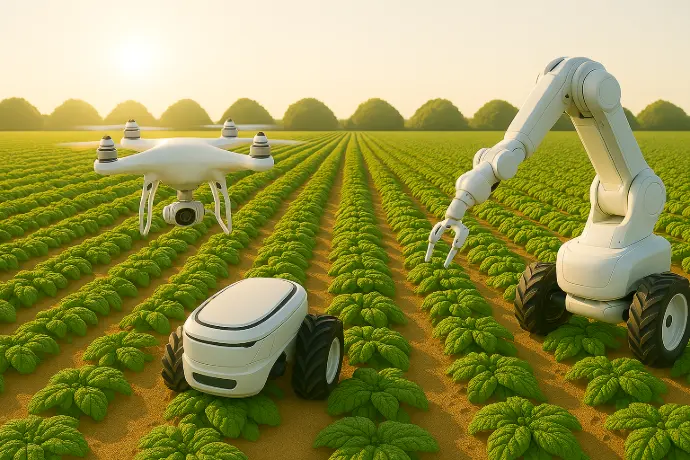
Artificial Intelligence in agriculture
Technology has become indispensable in any sector and agriculture is no exception. Proof of this is the Internet of Things (LoT). These are devices that are installed in the field and offer an analysis of the climatic conditions of the place at the time of sowing or fertilizing crops. The analysis offered by LoT on the state of the field is received instantly and contains indicators such as rainfall, temperature, humidity, plantation vigor, among others. Artificial intelligence in agriculture consists of aerial and aquatic drones, electrical, visual, olfactory and biological sensors, which create analysis files of the area with all possible information, depending on what needs to be known. It combines information from geographic positioning and genetic systems. In large crops, these machines are capable of monitoring pests that invade plantations; even intelligent machinery called cyber-insects have been created, which are drones that can control electric mobile cages.
The combination of artificial intelligence and field applications brings good results to the agricultural sector, making treatments and crop production more efficient. It is possible to store, encode and transfer genetic information through genetic editing. The laboratory incorporates a database that can be sent by email for constant verification. Previously, if there were samples to be analyzed, it was necessary to physically travel and a lot of time was lost. Now, with the software, it can reach any part of the world instantly. In Europe, there are already several companies that provide this hardware with applications for agriculture, although they are also applications that can be used in other sectors. Latin America has many green areas for agriculture, but in most cases, telecommunications operating companies cannot cover these areas; having an internet signal is essential for the service.
Influence of artificial intelligence in agriculture
Artificial intelligence is completely transforming the agricultural sector. Mainly, because it is able to increase crop yield by optimizing available resources, that is, from a sustainable and environmentally friendly perspective.
This optimization offers the possibility, for example, of cultivating land with obvious soil problems that would be unusable using conventional techniques. It is also significantly reducing the risk of human error.
After all, artificial intelligence systems operate from objective and reliable information collected by electronic devices. It is not surprising that more and more farmers are making the leap to using this new technology, although it is true that there is still a lot of work ahead to fully implement it.
Benefits of artificial intelligence in agriculture
Artificial intelligence systems in agriculture are capable of handling large volumes of data related to the crop in question. But not only that. They can also analyse them in real time and, if programmed for this purpose, make immediate decisions in the event of any potential problems or setbacks that may arise.
For example, this technology can permanently monitor soil moisture levels or carbon dioxide concentrations. From these, it will decide when to activate and deactivate the irrigation system or open the windows of a greenhouse without there being a person on hand to make the decision.
Precision agriculture and AI
Precision agriculture is the discipline that, based on the data collected, tries to make the best possible decisions at the right times and in the right places. That is, exactly when and where they are needed.
If we think about it, it makes no sense to go to the hospital for a stomach ache and be prescribed a general painkiller. Well, the same thing happens with precision agriculture: trying to solve a problem without knowing the exact time and place where it has occurred or can be generated only leads to wasting resources.
Without a doubt, this is the aspect in which artificial intelligence has the most influence within the agricultural sector. Of course, from different perspectives.
Pest control using AI
Pest control in crops using artificial intelligence is generally carried out by placing electronic traps. Despite its name, its objective is not to eliminate all insects and keep the plantation safe, but to identify their presence and typology.
Initially, these systems only detected the presence of insects when they passed through an infrared light. However, today they are able to determine the species in question by recognizing their wing flapping or other characteristic elements.
Once the species that is causing the pest or that has the potential to generate it is recognized, the algorithm is able to recommend or apply the appropriate treatments to combat or prevent it. What's more, thanks to machine learning, it will be able to make those same decisions or even better ones in the future.
Monitoring
As noted above, artificial intelligence relies on a series of devices to collect data. Basically, in sensors capable of determining the degree of soil humidity, the levels of nutrients present in the soil or the quality of the air inside a greenhouse, among many others.
The computer program collects and analyzes this information constantly and in real time. What's more, it gives the farmer the possibility of accessing it when he needs it, since it is generally managed on cloud storage platforms that can be accessed from anywhere with just an Internet connection. You can even configure the system to send you notifications under certain circumstances.
Mechanization of tasks
This is one of the most attractive aspects for farmers, since artificial intelligence saves them many hours of work and resources in hiring labor. From the collected data that we have referred to previously, the program can make its own decisions based on the instructions provided by the farmer.
Use of predictive maintenance
Another interesting possibility provided by machine learning is to predict what will happen in the future taking into account current data. We have already shown this with examples related to irrigation and pest control.
The primary objective of predictive maintenance is to prevent losses during the harvest. To do this, it is also essential to apply the concept to the machinery used within the plantation. Doing so is synonymous with avoiding breakdowns at the most inopportune times that can slow down the harvest or cause serious damage to the health of the plantation.