Biometrics
A biometric is an analysis of biological activities and phenomena. It is an examination that can focus on statistics or aim at measurement.
Recognition of individuals
Generally, the concept refers to the recording of measurements of living beings. By extension, biometry is known as the procedure that allows an individual to be recognized unequivocally based on certain features. A system can apply various techniques to verify a person's identity and thus provide access to a sector restricted to the general public. This set of techniques and resources are part of the field of biometrics.
The most common types
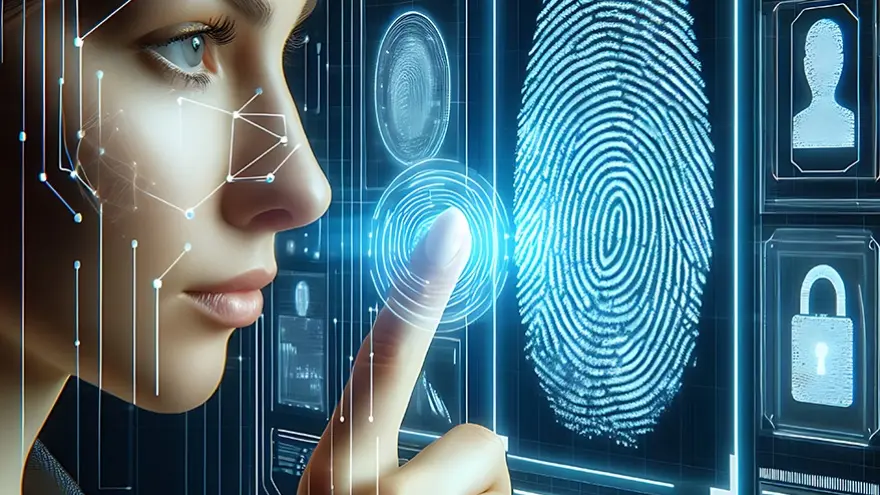
The study of the retina, fingerprints or palm of the hand, for example, is a tool that enables biometric recognition. In some cases, behavioural rather than biological characteristics are used, such as the way of walking or the signature.
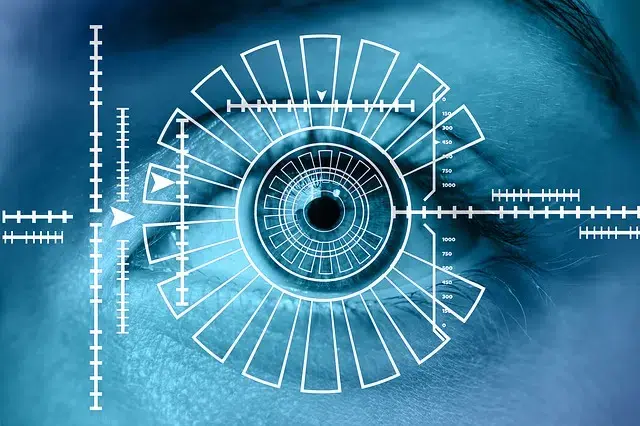
Iris recognition, on the other hand, is one of the most reliable methods. The iris is a membrane found in the eye that is responsible for regulating the size of the pupil, with the consequent control of the magnitude of light that penetrates it. This type of biometry should not be confused with the scanning of the retina, a tissue formed by neurons that communicate with the brain to send impulses: for the iris, its image is compared with a previously recorded one; for the retina, a beam is projected that carries out a complex capture process.
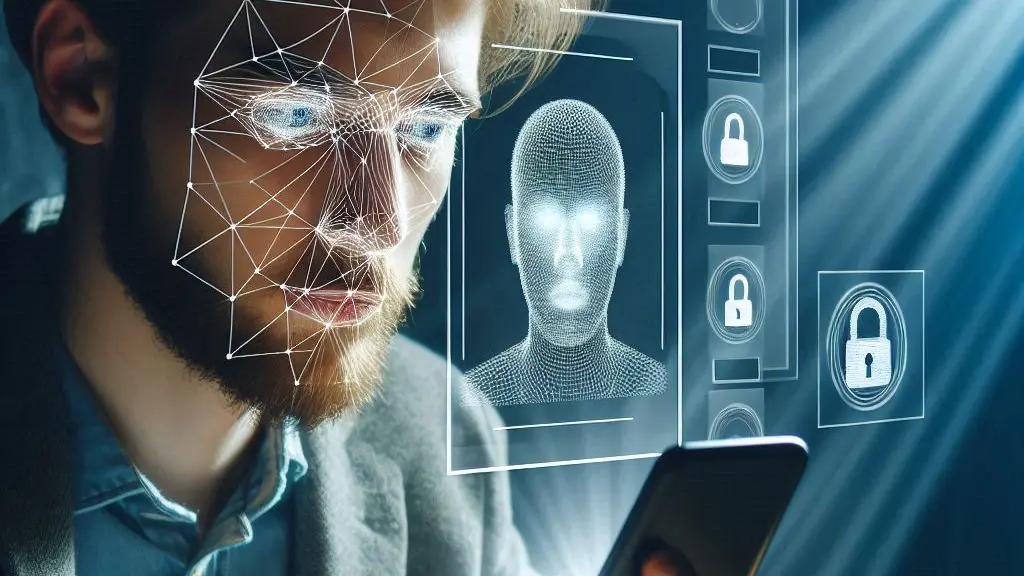
We can also mention facial recognition, which can be carried out in two or three dimensions, that is, capturing a flat or volumetric image. The first method can be manipulated by means of a photograph of the individual with access to the system, while the second requires the real face, so it is safer and more effective.
The basis is comparison
The operation of a biometric system is carried out through the comparison of data. First, the authorized person has to register a certain characteristic (such as a fingerprint). This information is processed through an algorithm and stored in a database. Then, each time the subject tries to enter the restricted area, he places his fingerprint on a reader. This fingerprint is compared with the database and, if it matches, he gains access. On the other hand, if another man tries to enter with his fingerprint, the records do not match and his request for entry is denied.
Comparison is a mechanism that we use every day, in our daily lives and in the most complex areas of science: we have in our memory an incalculable volume of information against which we analyze the data that surrounds us to make decisions. We recognize people by their face, their physical features, their way of walking, etc., precisely because we store all these characteristics in our brain in the first place.
Advantages and disadvantages
Biometrics offers several advantages: it does not require passwords, keys, magnetic cards, etc. For areas where security is crucial, it is suitable because only authorized persons pass the verification process. In the case of mobile phones, on the other hand, it saves time because it unlocks the screen by simply placing the finger on the reader or looking at the camera indicated for facial recognition.
Among its disadvantages, there are possible false negatives and false positives in recognition. As mentioned above, some methods are not infallible. In addition, while the theft of a password can be done without harming its owner, forcing him to pass a biometric test can lead to different degrees of violence.
What will be the consequences if a citizen revokes their biometric data?
If a citizen revokes their biometric data, the consequences will depend on the context in question (for example, whether it is for a security system or a government database). In general, revocation can prevent access to certain services or platforms that require biometrics, as well as increase the risk of identity theft if the revoked data is not properly protected or is leaked.
In detail, the consequences could include:
Inability to access certain services:
If a citizen revokes their biometric data, they may be unable to access certain security systems, such as unlocking their phone, accessing banking applications, or entering certain facilities.
Increased risk of identity theft:
If the revoked biometric data is not properly protected and accessible, it could be used to impersonate the individual.
Problems with government procedures and processes:
In some cases, biometrics may be necessary for identification and authentication in transactions with government agencies. Revocation could hinder or prevent these processes.
Impact on personal security:
If biometric data is revoked and is susceptible to use by third parties, this could pose a risk to personal security, such as unauthorized access to accounts, devices, or sensitive information.
Effects on privacy:
Although revoking biometric data can be an act of privacy protection, it can also create inconveniences and restrictions on access to services and technologies that rely on this information.
It is important to emphasize that the revocation of biometric data must be managed securely and confidentially to minimize risks. The person revoking their data must ensure that the information is properly removed from the systems and that it is not available for unauthorized use.